Dementia Disorder
Dementia Disorder
Dementia is a neuro cognitive disorder.
Generally it is a progressive cognition impairing disorder.
Progressive deterioration in cognition leads to impairment in social and occupational functioning.
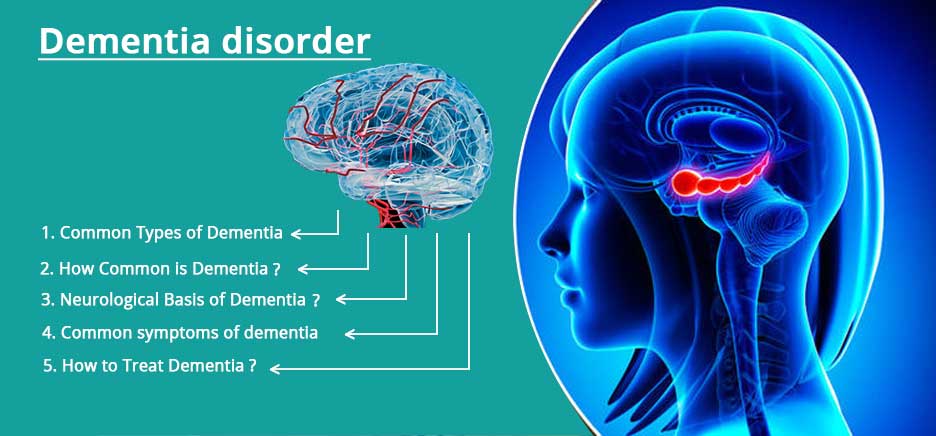
Common types of dementia:
Alzheimer, Lewy body, vascular, frontotemporal, due to brain trauma, parkinson’s, due to infections of brain, huntington’s, vitamin and nutritional deficiencies, alcohol and drugs. Most common variety is alzheimer’s disease.
How common is dementia?
Dementia increases with the age. At the age of 65 years almost 5% people have dementia but at the age of 85 years almost 30% people have dementia.
Neurological basis of dementia?
- Genetic
- Neurotransmitter (acetylcholine, glutamate)
- Aluminium toxicity
Common symptoms of dementia:
- Significant decline in cognitive processing (memory problem, attention, executive function, learning, language and social behaviour)
- Cognitive deficits interfere with independent activities of daily life.
- Changes in personality.
- Some people suffer from hallucinations, delusions, mood changes.
How to treat dementia?
- Medications
- Psychological counselling
In 10 to 15% cases dementia is reversible.